Firefighter injured fighting the Eicks Fire in Hidalgo County
(InciWeb)
SANTA FE, N.M. (AP) — A wildland firefighter was critically injured while fighting a wildfire on private land in southwestern New Mexico near the U.S.-Mexico border, state officials said Tuesday.
The firefighter works for the U.S. Forest Service and was injured Monday while fighting a fire in the Animas Mountains in Hidalgo County, the Forestry Division of the state Energy, Minerals, and Natural Resources Department said in a statement.
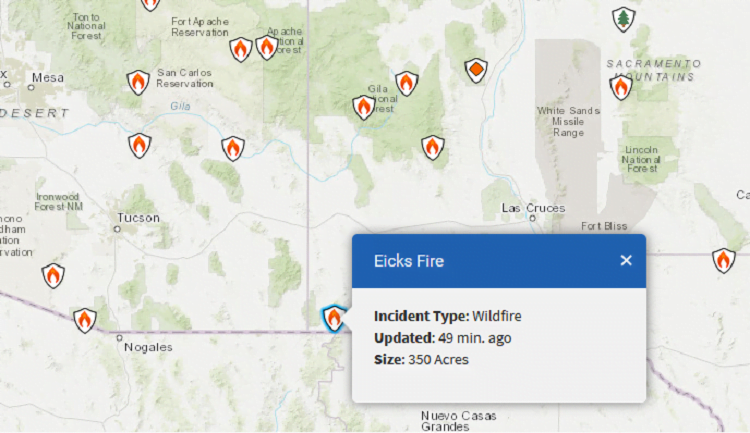
InciWeb: Eicks Fire Updates
The firefighter’s identity wasn’t released.
Division spokeswoman Wendy Mason said during a telephone interview that the firefighter is a member of an elite hotshots crew but that information on how the firefighter was injured wasn’t immediately available.
The firefighter was in critical condition Tuesday at a hospital in El Paso, Texas, according to the statement.
The fire had burned 350 acres in very rugged terrain along the Continental Divide and its case was under investigation, the statement said.
All contents © copyright 2021 The Associated Press. All rights reserved.




